Specifications: KL400 vs. ML4710 Deep Depletion
| KL400 | ML4710 DD | |
| Sensor Type | Back Illuminated CMOS | Back Illuminated CCD |
| Active Pixels | 2048 x 2048 | 1024 x 1024 |
| Pixel Size | 11 x 11 microns | 13 x 13 microns |
| Effective Area | 22.5 x 22.5 mm | 13.3 x 13.3 mm |
| Sensor Diagonal | 31.9 mm | 18.8 mm |
| Full Well Capacity | 90000 electrons | 100000 electrons |
| Frame Rate (rolling) | 24 fps HDR | 2 seconds per frame |
| Read Noise (Rolling) | 1.6 e- HDR (800 MHz) | 11 e- (700 kHz) |
| Dynamic Range | 86 dB HDR | 79 dB (700 kHz) |
| Peak QE | 95% (TVISB) | 93% (Midband) |
| Cooling | Air (Optional Liquid) | |
| Dark Current | 0.6 eps at -20C | 12 eps at -35C |
| Interface | USB 3.0 (Optional QSFP) | USB 2.0 |
| Data Bit Depth | 16 bit | |
| Optional Mount | F-mount | |
| Subarray Readout | Yes | |
| Electromechanical Shutter | Optional 45mm | Standard 45mm |
| External Trigger In/Out | Yes | |
| Software | FLI Pilot | FLIGrab |
| SDK | USB 2 (Open Source) | Kepler (Open Source) |
ProLine and MicroLine cameras using the e2v CCD47-10 deep depletion have been a standard for near infrared research for nearly a decade. The Kepler KL400 with back-illuminated CMOS provides an alternative with a higher signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and much higher frame rates.
The table below is a comparison of the Kepler KL400 TVISB and ML4710 deep depletion cameras, using a low flux value of 1 photon/pixel/second (without regard to pixel size) and the average quantum efficiency between 700 and 1000 nm. If flux to the smaller pixel of the KL400 is scaled by pixel area, the 400’s SNR remains 65% higher than the 4710.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio Comparison
| Exposure (sec) | 400 (1 pps) | 400(0.72 pps) | 4710 |
| 3600 | 27.7 | 21.3 | 9.9 |
| 1800 | 19.6 | 15.0 | 7.0 |
| 900 | 13.9 | 10.6 | 4.9 |
| 600 | 11.3 | 8.7 | 4.0 |
Summary: A Paradigm Shift
Though the ML4710 deep depletion has nearly 60% higher overall QE from 700 to 1000nm, the KL400’s lower noise and dark current give it a big advantage in signal-to-noise ratio.
| Exposure (sec) | 400 SNR | 4710 SNR |
| 1 x 600 | 11.3 | 5.2 |
| 5 x 120 | 11.2 | 5.1 |
| 10 x 60 | 11.1 | 4.9 |
Lower noise also means KL400 images can be stacked with little efffect on SNR, either automatically or after sorting for quality.
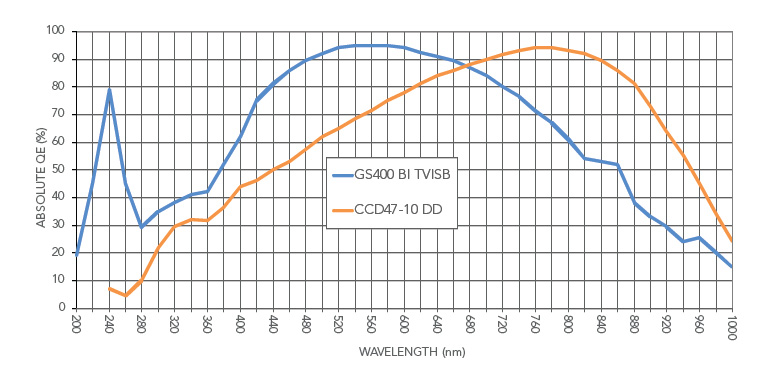
Quantum Efficiency: GSense400 TVISB vs e2v CCD4710 Deep Depletion